Digital Rockwell Hardness Testing System: Everything You Need to Know
Before you can choose between the various digital Rockwell hardness testing systems, understanding what they are and what they do is essential. In this article we'll cover everything you need to know about digital Rockwell hardness testing systems, including how a Digi-test differs from a conventional test, and why some brands are better than others. This post is a must-read for anyone looking to buy a new rockwell hardness tester!
What is the Rockwell Hardness Testing System?
First, let's discuss what hardness is. At its most basic, hardness refers to how easily a material scratches and wears away because of contact with another material. In metals, a digital Rockwell hardness testing system can be used to determine how ductile a metal is, which determines the amount of force that needs to be applied for it to break. It can also be used to determine how tough or brittle a metal is and how well it resists compression and tension (the two main types of stress that can be applied to any solid material). When measuring the degree of hardness in metals, tests are often performed using a diamond-tipped pin inserted into the metal while it sits on a calibrated chuck plate.
Testing is done by stroking the sample with the pin in a defined manner. Wider strokes create deeper indentations and thinner strokes leave shallow marks. Measuring this depth is how hardness is determined. The hardness number (expressed as Rockwell hardness) corresponds to the depth in thousands of an inch (or millimeters). So an "Rc" reading of 100 would mean that 100 thousandths of an inch were removed by the Rockwell tester pin when stroked across the material.
What this means is that a higher Rc number actually means that less force was needed to make it scratch, and conversely, a lower Rc number means that more force was required to make it scratch. It should be noted that different machines, even those by the same manufacturer, can read a material differently. So having a number is only as good as the machine that reads it.
There are two different scales used to express hardness: HR and HRC. On the HR scale, numbers above 66 represent low hardness, while numbers below 66 represent high hardness. On the HRC scale (a slightly newer scale introduced in 1960), numbers above 70 represent low hardness while numbers below 70 represent high hardness. While both scales are typically used interchangeably, many experts recommend using HRC readings whenever possible to avoid confusion.
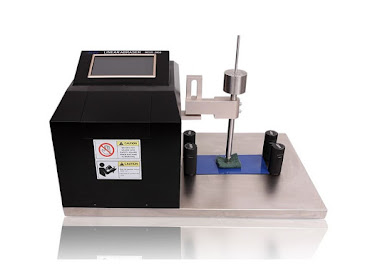
A Digital Rockwell Hardness Testing System
Digital rockwell hardness testing machines fall into two categories: Digi-tests and conventional tests. Digi-tests are most commonly used in the metalworking industry for assembly and machining operations, while conventional machines are used by machinists and other craftspeople who do not use heavy machinery. While they both work in a similar fashion, they each have their advantages and disadvantages for different types of users.
Digi-Tests vs Conventional Tests: Which One Is Right For You?
When comparing the two, it's important to understand how each works. To test a sample, the machine is inserted into the chuck (much like how a lathe would be). The sample is then placed onto the chuck plate and the equipment's motor is turned on. The pin inside the device is then stroked across the sample in order to create a reading. Conventional machines use a hand-operated lever, while Digi-tests rely on motors and an electronic component called a "stimulus/response" unit, which controls how the pin moves across the sample.
Digi-tests are obviously more convenient for assembly line jobs or any other situation where time is of the essence. They're important in industry because they help eliminate human error from hardness tests, thus ensuring consistency.
About TestCoat:
For many years, TestCoat has been a trustworthy partner and leader in the supply and distribution of inspection equipment, laboratory & physical test equipment for the coatings and paint industries. We supply non-destructive quality control and testing instruments such as washability tester, Paint thickness Mil Gauges, Gloss meters, portable Rockwell hardness tester, laboratory mixersviscometers, film applicatorsdrying time recorder, cupping testers, Wet scrub abrasion testers, Coating inspection kits with advanced technology, and of the highest standards.
What this means is that a higher Rc number actually means that less force was needed to make it scratch, and conversely, a lower Rc number means that more force was required to make it scratch. It should be noted that different machines, even those by the same manufacturer, can read a material differently. So having a number is only as good as the machine that reads it.
There are two different scales used to express hardness: HR and HRC. On the HR scale, numbers above 66 represent low hardness, while numbers below 66 represent high hardness. On the HRC scale (a slightly newer scale introduced in 1960), numbers above 70 represent low hardness while numbers below 70 represent high hardness. While both scales are typically used interchangeably, many experts recommend using HRC readings whenever possible to avoid confusion.
A Digital Rockwell Hardness Testing System
Digital rockwell hardness testing machines fall into two categories: Digi-tests and conventional tests. Digi-tests are most commonly used in the metalworking industry for assembly and machining operations, while conventional machines are used by machinists and other craftspeople who do not use heavy machinery. While they both work in a similar fashion, they each have their advantages and disadvantages for different types of users.
Digi-Tests vs Conventional Tests: Which One Is Right For You?
When comparing the two, it's important to understand how each works. To test a sample, the machine is inserted into the chuck (much like how a lathe would be). The sample is then placed onto the chuck plate and the equipment's motor is turned on. The pin inside the device is then stroked across the sample in order to create a reading. Conventional machines use a hand-operated lever, while Digi-tests rely on motors and an electronic component called a "stimulus/response" unit, which controls how the pin moves across the sample.
Digi-tests are obviously more convenient for assembly line jobs or any other situation where time is of the essence. They're important in industry because they help eliminate human error from hardness tests, thus ensuring consistency.
About TestCoat:
For many years, TestCoat has been a trustworthy partner and leader in the supply and distribution of inspection equipment, laboratory & physical test equipment for the coatings and paint industries. We supply non-destructive quality control and testing instruments such as washability tester, Paint thickness Mil Gauges, Gloss meters, portable Rockwell hardness tester, laboratory mixersviscometers, film applicatorsdrying time recorder, cupping testers, Wet scrub abrasion testers, Coating inspection kits with advanced technology, and of the highest standards.
For more information, visit https://www.testcoat-usa.com/



Comments
Post a Comment